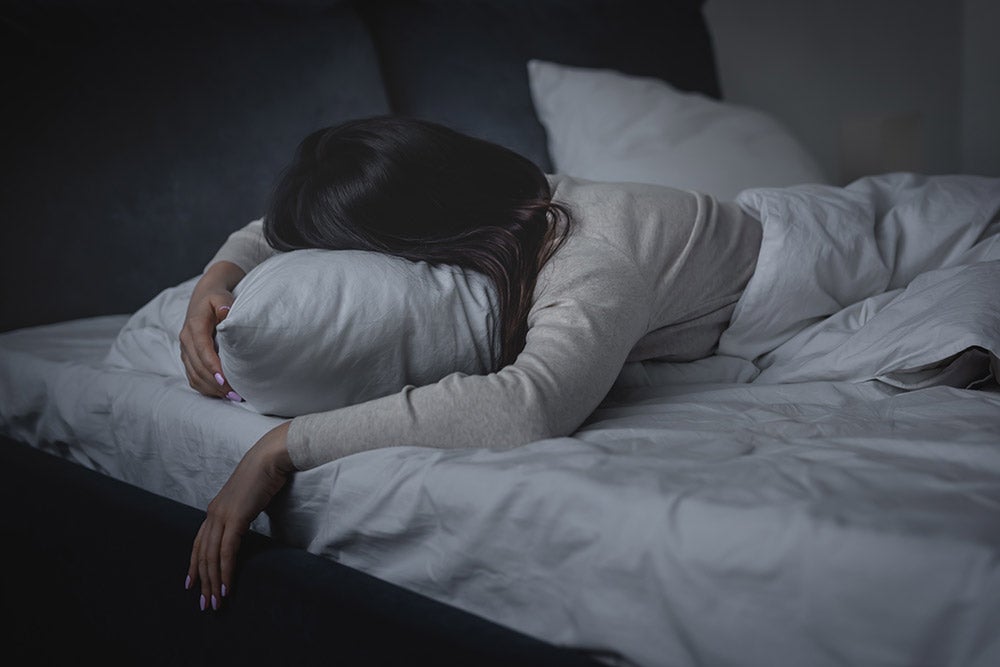
Sweating is commonly associated with weather conditions or exercise. If you are sweating at night and it is not because of any of these two factors, there might be another in mind. You might have hyperhidrosis.
Hyperhidrosis is a condition that makes you sweat profusely at night to the extent that it can hamper your sleep.
Although sweating from extreme weather conditions or exercise can interfere with your sleep, sweating due to hyperhidrosis is a condition you might want to look into.
Hyperhidrosis is a condition that occurs mainly among older adults, although anyone can suffer from it. Research reveals that 12% of the population may experience the condition. Night sweats occur in different forms.
What are the types of hyperhidrosis?
Primary hyperhidrosis
Primary hyperhidrosis is also called focal hyperhidrosis. It occurs with no medical motivation for it. This form of night sweats is motivated by genetic factors. The patient's nervous system signals the sweat glands to produce sweat in excess. There are no medical undertones to primary night sweats that can cause one to worry.
Primary night sweats are usually associated with such areas of the body as the face, feet, and hands. However, some people may experience sweating in more than one of these areas at the same time.
Secondary hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis has medical reasons for it, and it occurs all over the body rather than in some areas. there are several reasons for this form of night sweat, including:
Menopause
The hormonal change in women as menopause sets in can cause excessive sweats at night. Women in the menopausal stage can experience a decreased level of estrogen and other changes in their bodies. Excessive sweating has been linked to hot flashes, which signals menopause.
Thyroid disorders
Thyroid disorders can result in over-activeness and signal high metabolism. The thyroid is situated at the front of the throat. It is responsible for producing hormones for metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, weight, etc. If the thyroid suffers from hyperthyroidism, there will be increased activity and, consequently, excessive sweat.
Heart conditions
A heart condition like a heart attack is another cause of secondary hyperhidrosis. Heart failure can cause an excess buildup of fluid in the body. The body will try to rid itself of this excess fluid buildup by sweating. Also, when the heart cannot pump enough blood to satisfy the needs of the body, it will put the body under stress as it tries to manage the amount of blood the heart can pump. This stress can also cause excessive sweating.
Sleep disorders
Sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea, OSA, can cause night sweats. OSA restricts breathing and can cause nocturnal sweating.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a blood sugar impairment that can result in excessive sweating at night. Diabetes occurs when the blood sugar is too high, which is hyperglycemia. This situation can damage some nerves in the body. If the nerves controlling sweat are damaged, the result can be hyperhidrosis. Also, low blood sugar is a cause of hyperhidrosis.
Infection
Infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses such as endocarditis can also cause hyperhidrosis. Endocarditis is an infection and inflammation of the heart's lining. One of the common symptoms of this condition is excessive sweating, especially at night. Infections like abscesses, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, and HIV can also cause excessive sweating.
Medications can also cause hyperhidrosis
Some medications have side effects that include excessive sweating. Some of them are:
Antidepressants
Antidepressants usually have excessive sweating as a side effect. These medications include antidepressants like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, bupropion (Wellbutrin), and venlafaxine (Effexor).
Migraine medications
Triptan migraine medications such as rizatriptan (Maxalt), sumatriptan (Imitrex), eletriptan (Relpax), and Frovatriptan (Frova) can cause sweating. This is because these medications, like SSRIs, can improve serotonin production. These medications can also lead to serotonin syndrome.
Pain relievers
Most over-the-counter pain relievers such as aspirin and ibuprofen can lead to sweating. These medicines reduce fever by the release of heat through the skin. This can lead to sweating.
Medication for GERD
Medications for gastroesophageal reflux called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can cause excess sweating. These medications include lansoprazole (Prevacid) and omeprazole (Prilosec). There is little reason why these medications cause secondary hyperhidrosis. However, when the patients stop taking the medications, the excessive usually stops.
Glaucoma medications
Experts have revealed that topical antiglaucoma agent, latanoprost, can cause excessive sweating in patients. Medical observations reveal that patients who use the medication complain of excessive sweating up to the extent of having their whole bodies drenched. When the medication is withdrawn, the excessive sweating stops. There is no profound medical explanation for sweating, but it is a side effect in young people and adults.
Alzheimer's and Parkinson's medications
Parkinson's disease is usually treated with ropinirole which is notable for causing sweat. Ropinirole makes dopamine receptors more active and produces sweat.
Cancer medications
Breast cancer medications like tamoxifen (soltamox), exemestane (Aromasin), anastrozole (Arimidex), and several others can cause hyperhidrosis. These medicines have anti-estrogen content that leads to excessive sweating as side effects.
Hyperhidrosis occurs among young people and adults. From research, it is discovered that out of ten people who experience hyperhidrosis, fewer than four are likely to discuss it. However, it is essential to know what causes it and try to prevent it. With this guide, you have a better idea of the condition.